Banking on consequences: an examination of penalties imposed on financial institutions
- Team WhiteSight
- 3 mins read
- Insights, Traditional Finance
Table of Contents
As the backbone of national and global financial systems, banks are held to the highest standards of accountability, financial stability and fairness. However, the consequences can be harsh and far-reaching when these standards are not met.
This post is only available to members.
Already a subscriber? Log in to Access
Unlock this blog
Gain exclusive access to this blog alone.
Radar Subscription
Select a membership plan that resonates with your
goals and aspirations.
Not Ready to Subscribe?
Experience a taste of our expert research with a complimentary guest account.
We publish new research regularly. Subscribe to stay updated.
No spam.
Only the best in class fintech analysis.
Related Posts
- Kshitija Kaur and Sanjeev Kumar
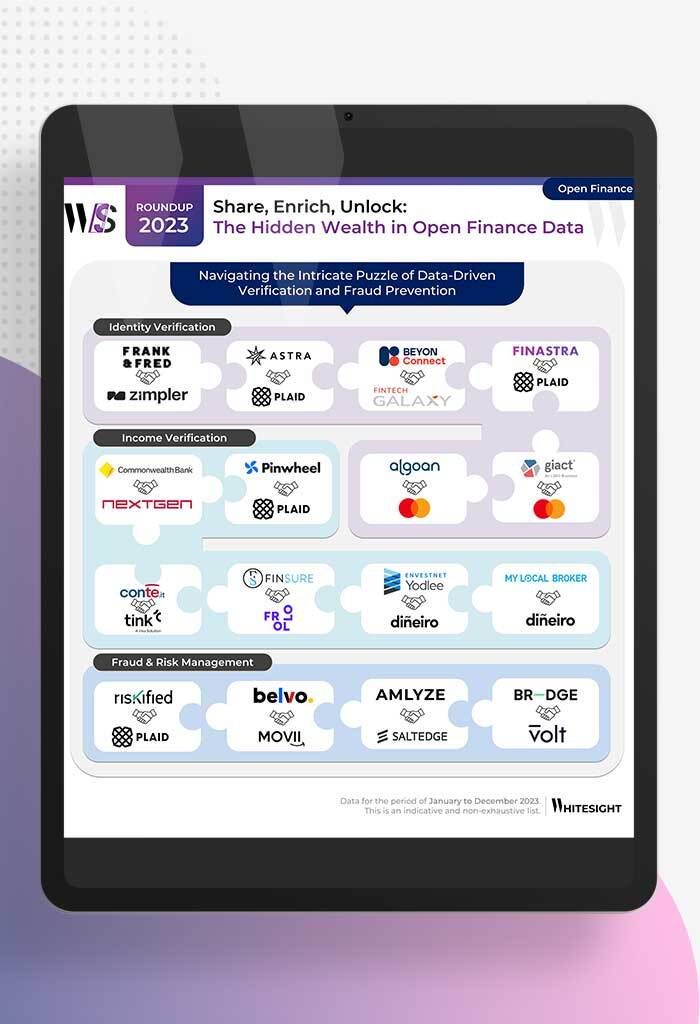
From Data Streams to Enriched Data Fountains Remember the early days of plumbing? Water flowed freely, but its quality was...
- Samridhi Singh and Sanjeev Kumar
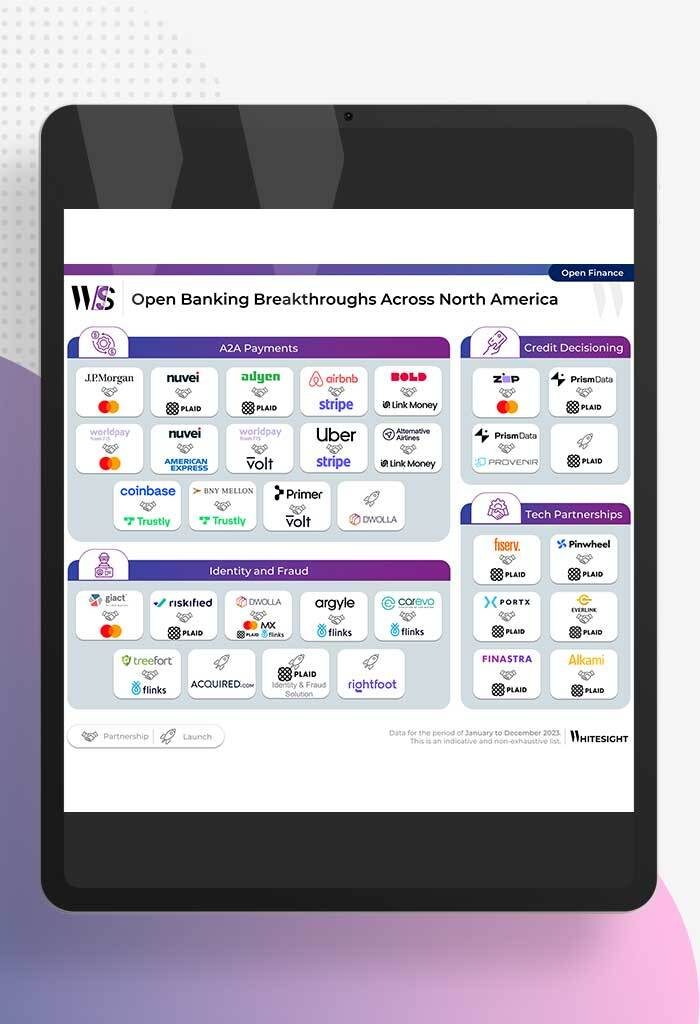
North America’s Open Sesame: Use Cases Bloom Open banking has garnered significant attention in recent years, and at Whitesight, we’ve...
- Samridhi Singh and Sanjeev Kumar
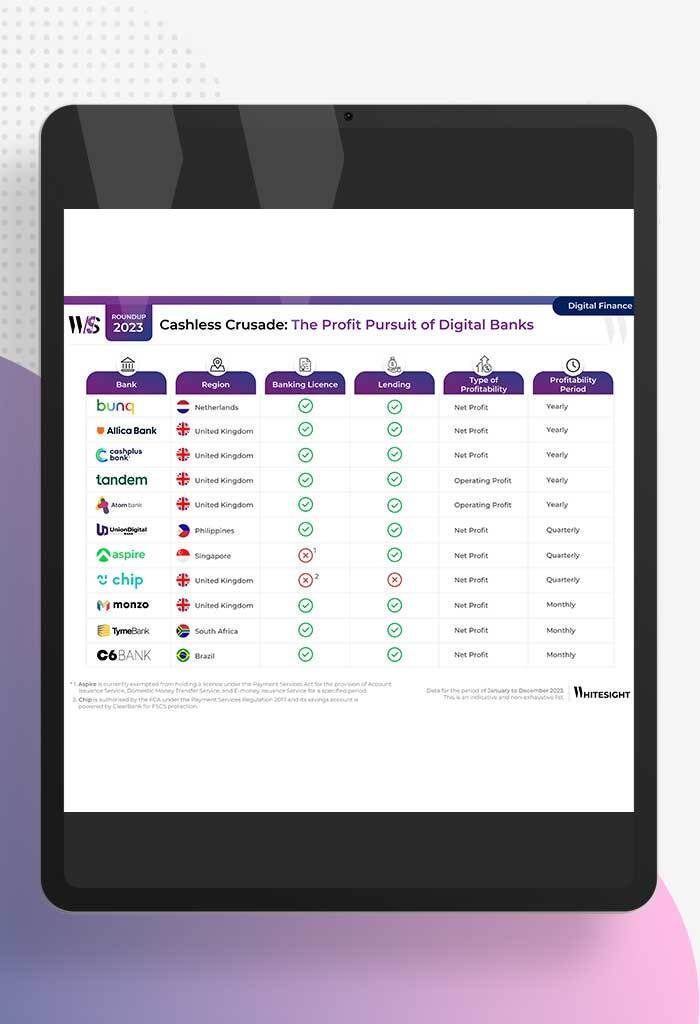
Profitability Unlocked: Licences, Service, and Survival The rise of digital banks has sparked a paradigm shift in how we perceive...
- Sanjeev Kumar and Risav Chakraborty
High stakes in the gambling sector The online gambling industry is booming, with a projected market size of $107.3B by...
- Sanjeev Kumar and Risav Chakraborty
Open Banking-led Transformation of Traditional Lending In 2023, a wave of innovation swept through the lending industry, thanks to several...
- Sanjeev Kumar
Unmasking Open Banking’s Game Changers in 2023 2023 has been a pivotal year in the world of open banking, marked...